这场我们队发挥得还不错,最终$rk131$,还得到了教练的表扬(
浅录一下由我码的几个题
1006-Maex
题目描述
给出以$1$为根的树,你可以给每个点赋不同的值,我们定义该点的贡献为以这个点为根节点的子树内的$MEX$(最小未出现过的数),求所有节点贡献和的最大值。
思路
$dp_x$代表以$x$为根节点的子树最大贡献和。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;using LL = long long ;const int N = 5e5 + 5 , MOD = 998244353 , INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ;int n;vector< int > adj[N]; int num, siz[N];LL dp[N]; void dfs (int x, int p) siz[x] = 1 ; for (auto &y : adj[x]) { if (y ^ p) { dfs (y, x); siz[x] += siz[y]; dp[x] = max (dp[x], dp[y]); } } dp[x] += siz[x]; } void solve () cin >> n; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++ i) { adj[i].clear (); siz[i] = dp[i] = 0 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i < n; ++ i) { int u, v; cin >> u >> v; adj[u].push_back (v); adj[v].push_back (u); } dfs (1 , 0 ); cout << dp[1 ] << '\n' ; } signed main () cin.tie (nullptr )->sync_with_stdio (false ); int t; cin >> t; while (t -- ) { solve (); } return 0 ; }
1007-Shinobu loves trip
题目描述
有$n$条旅游路线,每条路线有一个起点$s$以及旅行天数$d$,一开始在起点,第$i$天在$s + a \times d \mod p$。
$q$次询问,每次询问有多少条路线会经过$x$。
思路
若第 $i$ 条路线经过 $x$ ,那么满足 $s_i + a^k \mod p \equiv x$,移项得 $a^k \mod p \equiv \frac {x}{s_i} \mod p$。也就是说存在 $0 \leq k \leq d_i$ 满足前面的等式。
我们可以预处理出 $a^i \mod p$ 最先出现的 $i$,然后查询时我们对每一条路线询问 $\frac{x}{s_i} \mod p$ 最早出现时间是否 $\leq d_i$。
注意,若起点为 $0$ 的话,整条路线都是重复在走 $0$ 这个点,所以我们要特判一下。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 #include <iostream> #include <unordered_map> using namespace std;using LL = long long ;const int N = 1005 , MOD = 998244353 , INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ;int p, a, n, q;int s[N], d[N], inv[N];LL ksm (LL x, LL y, LL P) { LL res = 1 ; for (; y; y >>= 1 , x = x * x % P) { if (y & 1 ) { res = res * x % P; } } return res; } void solve () cin >> p >> a >> n >> q; unordered_map< int , int > fir; for (int i = 1 , x = 1 ; i <= 200005 ; ++ i, x = (LL)x * a % p) { if (!fir[x]) { fir[x] = i; } } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++ i) { cin >> s[i] >> d[i]; ++ d[i]; inv[i] = ksm (s[i], p - 2 , p); } while (q -- ) { int x, ans = 0 ; cin >> x; if ( x == 0 ) { for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++ i) { if ( s[i] == 0 ) ++ ans; } } else { for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++ i) { int pos = (LL)x * inv[i] % p; if (fir[pos] && fir[pos] <= d[i]) { ++ ans; } } } cout << ans << '\n' ; } } signed main () cin.tie (nullptr )->sync_with_stdio (false ); int t; cin >> t; while (t -- ) { solve (); } return 0 ; }
1010-Planar graph
题目描述
给出一张平面图,求用数量最少且编号最小的边使不同平面之间能够连通。
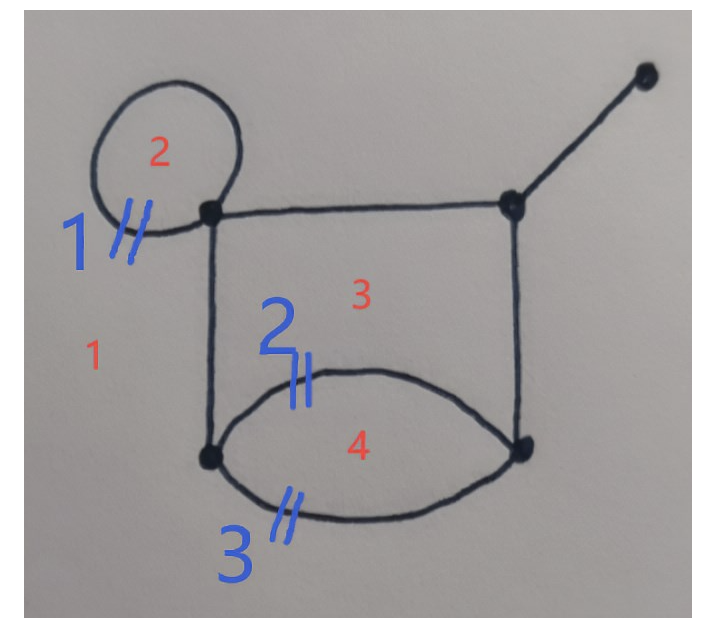
比如这张图就把整个平面分割成了 $4$ 个部分,使用编号为 $1、2、3$ 的边能够让这 $4$ 个部分连通。
思路
首先分割平面的条件为产生闭环,手玩几个样例之后我们会发现其实答案的个数其实是固定的,就是分割的平面的个数减一,是不是很像 $Kruskal$ ?因为要求边的编号最小,所以我们可以倒着加边,当两个端点在连接之前就已经在一块了,那么这时就产生了闭环,说明新的平面要产生了,这时这条边就是当前的最优边,然后重复这个过程。
很像吐槽的是,$hdu$ 的评测机居然会把 $RE$ 判成 $WA$,让我以为我想错了,结果数组开大一倍就过了…
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;using LL = long long ;const int N = 1e5 + 5 , MOD = 998244353 , INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ;int n, m, f[N], u[N * 2 ], v[N * 2 ];int find (int x) return f[x] == x ? x : f[x] = find (f[x]); } void solve () cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; ++ i) { cin >> u[i] >> v[i]; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++ i) { f[i] = i; } vector< int > idx; for (int i = m; i >= 1 ; -- i) { int fx = find (u[i]), fy = find (v[i]); if (fx == fy) { idx.push_back (i); } else { f[fx] = fy; } } cout << idx.size () << '\n' ; sort (idx.begin (), idx.end ()); for (auto &x : idx) { cout << x << ' ' ; } cout << '\n' ; } signed main () cin.tie (nullptr )->sync_with_stdio (false ); int t; cin >> t; while (t -- ) { solve (); } return 0 ; }
1012-Loop
题目描述
给出一个长度为 $n$ 的序列,你可以进行 $k$ 次操作,每次操作你都可以选择一个区间 $[l,r]$,让 $a_{i+1}=a_i(l \leq i \leq r-1)$,然后让 $a_l$ 等于原来的 $a_r$。
求$k$次操作后,字典序最大的序列是多少。
思路
首先,我们考虑什么时候应该将 $a_i$ 挪到后面去,当后面有 $a_j$ 大于 $a_i$ 并且 $a_i$ 是前面小于 $a_j$ 的数里最小的数,这时我们就可以将 $a_i$ 挪到后面,然后将 $k$ 减 $1$。我们先不管将这些数挪到哪里,先将它们存起来。
当 $k$ 减到 $0$ 时,我们考虑将之前存起来的数插到剩余序列里去,我们贪心地将它们从大到小地插入。
我们考虑什么时候插入是最优的,设剩余的数组成的序列为 $b$ ,拿出来的数里当前最大的数为 $x$ ,当 $b_i \ge x >b_{i+1}$ 时我们将 $x$ 插入到 $b_i$ 和 $b_{i+1}$ 之间是最优的。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;using LL = long long ;const int N = 3e5 + 5 , MOD = 998244353 , INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ;int n, k, a[N];bool vis[N];void solve () cin >> n >> k; set< pair< int , int > > st; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++ i) { vis[i] = false ; } vector< int > a1, a2; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++ i) { cin >> a[i]; while (k && !st.empty () && st.begin ()->first < a[i]) { vis[st.begin ()->second] = true ; a2.push_back (st.begin ()->first); st.erase (st.begin ()); -- k; } st.insert ({a[i], i}); } while (k && !st.empty ()) { vis[st.begin ()->second] = true ; a2.push_back (st.begin ()->first); st.erase (st.begin ()); -- k; } sort (a2.begin (), a2.end ()); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++ i) { if (!vis[i]) { a1.push_back (a[i]); } } vector< int > ans; for (int i = 0 ; i < a1.size (); ++ i) { ans.push_back (a1[i]); if (i + 1 < a1.size ()) { while (!a2.empty () && a1[i] >= a2.back () && a2.back () > a1[i + 1 ]) { ans.push_back (a2.back ()); a2.pop_back (); } } } while (!a2.empty ()) { ans.push_back (a2.back ()); a2.pop_back (); } for (int i = 0 ; i < ans.size (); ++ i) { cout << ans[i] << " \n" [i + 1 == ans.size ()]; } } signed main () cin.tie (nullptr )->sync_with_stdio (false ); int t; cin >> t; while (t -- ) { solve (); } return 0 ; }